Securing Your Digital Identity: Key Insights from Cisco Talos 2024 Year in Review
Patch, Protect, Prevent: Key Lessons from Cisco Talos’ 2024 Findings
Securing Your Digital Identity: Key Insights from Cisco Talos 2024 Year in Review
The recently released Cisco Talos Year in Review report for 2024 provides critical insights into the evolving cybersecurity threats organizations faced throughout the year. This comprehensive analysis draws from telemetry collected from over 46 million devices across 193 countries, processing more than 886 billion security events daily from January 1, 2024 to December 31, 2024.
Let’s dive into the key findings that should inform your security strategy for 2025.
 Identity-Based Threats Dominated 2024
Identity-Based Threats Dominated 2024
Identity-based attacks were the predominant threat in 2024, appearing in 60% of all Cisco Talos incident response cases. For the second consecutive year, valid accounts remained the top initial access vector, as adversaries increasingly opted to simply log in rather than deploy more complex methods.
Why are identity-based attacks so appealing to attackers? They’re difficult to detect, easy to carry out, and enable subsequent malicious operations. These attacks target the unique digital identity of users, organizations, or machines by exploiting a range of identifiers including login credentials, API keys, encryption keys, session tokens, and digital certificates.
Almost half of all identity-based attacks specifically targeted Active Directory, with another 20% focusing on cloud applications. Many successful attacks occurred in environments with misconfigured security products or policies that didn’t align with recommended best practices.
 Ransomware Trends
Ransomware Trends
The education sector was hit hardest by ransomware in 2024, continuing a trend from previous years. Higher education entities were particularly targeted, likely due to the valuable data they house, such as proprietary research. Other heavily targeted sectors included public administration, manufacturing, and healthcare.
Ransomware operators showed clear patterns in their tactics:
- They prioritized disabling security solutions early in their operations, succeeding nearly 50% of the time
- Valid accounts were used for initial access in 69% of cases
- Attacks appeared more frequent during spring and summer months, potentially taking advantage of vacation periods
- LockBit remained the most active ransomware group for the third consecutive year, while newcomer RansomHub quickly rose to the second spot
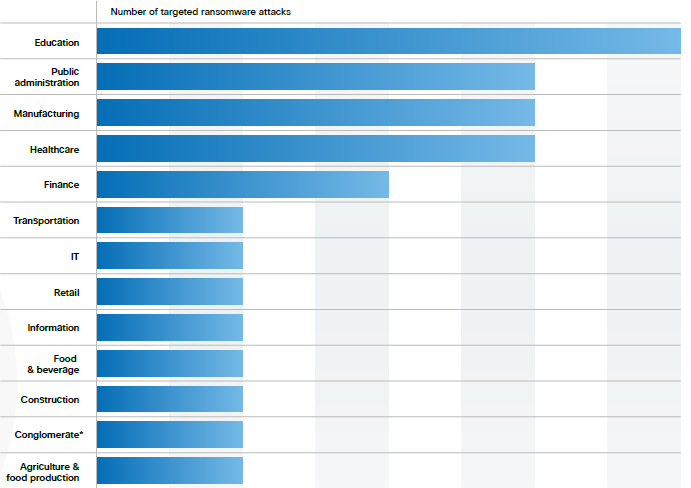
(Ransomware Targeted Sectors – Source: Cisco Talos Year In Review 2024)
 Multi-Factor Authentication Challenges
Multi-Factor Authentication Challenges
MFA weakness was the leading security gap observed in Cisco Talos incident response data. A quarter of these issues stemmed from complete lack of MFA enrollment, while other problems included incomplete implementation and absence of MFA on VPN services.
Identity and access management (IAM) applications were the most frequently targeted in MFA attacks, accounting for nearly a quarter of related incidents. Together with network security, authentication and networking, and remote access applications, these made up over 50% of incidents targeting MFA deployments.
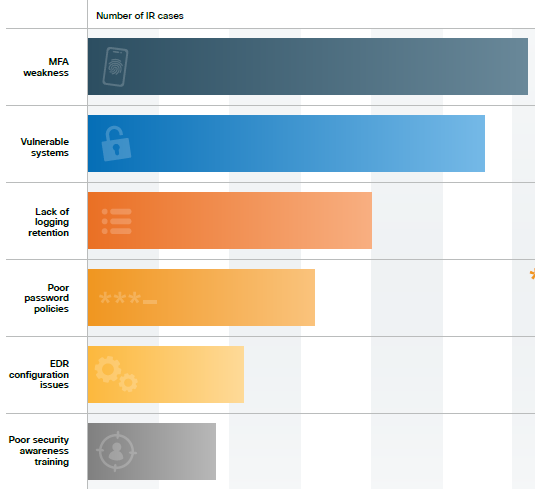
(Top Security Weaknesses in Talos IR Cases – Source: Cisco Talos Year In Review 2024)
 Top Vulnerabilities and Security Weaknesses
Top Vulnerabilities and Security Weaknesses
Most of the top-targeted vulnerabilities in 2024 were older CVEs that have been public for several years. Notably, four of the top twelve vulnerabilities were published a decade ago, and the notorious Log4j vulnerabilities from 2021 also remained heavily targeted.
All these vulnerabilities impact widely used software and hardware, creating an incredibly broad attack surface. For example, the PHP vulnerabilities affect 75-80% of the world’s two billion websites, while Bash vulnerabilities (known as “Shellshock”) impact many Linux/UNIX systems and older MacOS versions. This highlights how organizations continue to struggle with basic patch management, leaving systems vulnerable to well-known exploits.
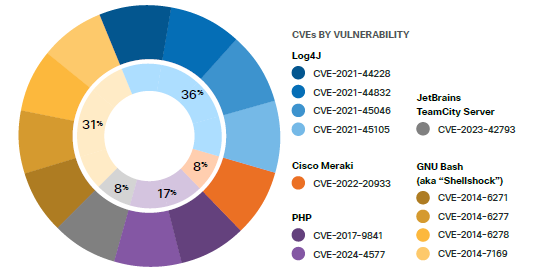
(Top-Targeted Vulnerabilities in 2024 – Source: Cisco Talos Year In Review 2024)
 Email Threats and Social Engineering
Email Threats and Social Engineering
Phishing continued to be a primary method of compromise, with embedded malicious links appearing more successful than other techniques like email attachments or voice phishing. Attackers frequently spoofed well-known brands in their phishing attempts, with Microsoft Outlook being the most commonly impersonated.
Rather than using urgent or time-sensitive subject lines, threat actors increasingly opted for ordinary, common words that would look benign in users’ inboxes. However, they remained attuned to major national events, incorporating themes like the 2024 presidential race into their phishing campaigns.
 Tools and Techniques
Tools and Techniques
Attackers predominantly relied on living-off-the-land binaries (LoLBins) rather than commercial or open-source tools. These native utilities, such as PSExec, PowerShell, and RDP, allow adversaries to blend in with regular network traffic and avoid triggering security solutions.
When commercial or open-source tools were employed, they often focused on credential dumping capabilities. For example, DonPAPI was newly observed in Talos incident response engagements, which automates credential dumping remotely on multiple Windows computers.
 AI Threats
AI Threats
While AI didn’t significantly enhance attackers’ capabilities in 2024, threat actors did leverage it for social engineering and task automation. The accessibility of generative AI tools contributed to more sophisticated social engineering attacks, helping criminals create convincing phishing campaigns.
Looking ahead to 2025, Cisco anticipates several developments in the AI threat space:
- The rise of agentic AI systems that can act autonomously
- Continued social engineering at scale
- Automated vulnerability discovery and exploitation
- New capabilities that can compromise AI models, systems, and infrastructure
 How CinchOps Can Help Secure Your Business
How CinchOps Can Help Secure Your Business
In light of these findings, partnering with a security-focused IT provider like CinchOps is more crucial than ever. Here’s how we can help strengthen your security posture:
- Identity Management: Implement robust identity solutions with proper MFA deployment, focusing on eliminating the weaknesses highlighted in the Cisco report.
- Security Monitoring: 24/7 monitoring services help detect suspicious activities, especially those originating from compromised legitimate accounts.
- Patch Management: Ensure your systems are updated against known vulnerabilities, preventing attacks that exploit older, unpatched CVEs.
- Security Awareness Training: Train your team to recognize phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics, creating a human firewall against these common attack vectors.
- Active Directory Security: Implement best practices for securing your Active Directory environment, a critical target identified in the report.
- Ransomware Protection: Comprehensive backup and disaster recovery solutions help mitigate the impact of potential ransomware attacks.
- Regular Security Assessments: Conduct periodic evaluations of your security posture to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Discover more about our enterprise-grade and business protecting cybersecurity services on our Cybersecuritypage.
Don’t wait until your organization becomes a statistic in next year’s security report. Contact CinchOps today to strengthen your defenses against the evolving threat environment.
FREE CYBERSECURITY ASSESSMENT



