GhostPenguin: The Zero-Detection Linux Backdoor Evading Security for Months
How Trend Micro Researchers Used AI To Uncover The GhostPenguin Backdoor – How Custom-Built Malware Bypasses Signature-Based Detection Systems
GhostPenguin: The Zero-Detection Linux Backdoor Evading Security for Months
TL;DR: GhostPenguin is a newly discovered Linux backdoor that remained undetected on VirusTotal for over four months. This multi-threaded C++ malware uses RC5-encrypted UDP communication to provide attackers with remote shell access and full file system control, posing serious risks to Linux server environments.
![]()
 A Stealthy Threat Emerges from the Shadows
A Stealthy Threat Emerges from the Shadows
Trend Micro researchers have uncovered a previously undocumented Linux backdoor that managed to fly under the radar of every major antivirus engine for more than four months. Dubbed GhostPenguin, this multi-threaded malware represents a concerning evolution in threat actor capabilities – one where attackers are building their tools entirely from scratch to avoid detection signatures based on known code libraries and patterns.
What makes GhostPenguin particularly troubling is how it was discovered. Traditional detection methods failed completely. It took Trend Micro’s AI-driven, automated threat hunting pipeline analyzing zero-detection samples from VirusTotal to finally bring this backdoor into the light. Security researcher Aliakbar Zahravi and the Trend Research team used advanced machine learning techniques to profile suspicious files, ultimately exposing GhostPenguin after it had remained completely invisible to security tools since its submission to VirusTotal on July 7, 2025.
 Technical Breakdown: How GhostPenguin Operates
Technical Breakdown: How GhostPenguin Operates
GhostPenguin is a sophisticated piece of malware that demonstrates careful engineering to remain inconspicuous. Here’s what security teams need to understand about its operation:
- Programming and Architecture: Written in C++, GhostPenguin operates as a multi-threaded backdoor targeting Linux systems. Its architecture separates functions into distinct threads handling registration, heartbeat signaling, command reception, and data transmission.
- Encrypted Communications: All command-and-control traffic flows over UDP port 53, typically associated with DNS queries. The malware employs RC5 encryption using a 16-byte session ID obtained during an initial handshake with the C&C server.
- Session Establishment: Upon execution, the malware sends an unencrypted UDP packet requesting a session ID from the server. Once received, this ID serves as the encryption key for all subsequent communications.
- System Reconnaissance: GhostPenguin harvests extensive system information including LAN IP address, default gateway, OS distribution details, hostname, current username, architecture type, and process ID.
- Instance Control: The backdoor creates a hidden file named “.temp” in the user’s home directory containing its process ID, preventing multiple instances from running simultaneously.
- Heartbeat Mechanism: To maintain its connection, the malware sends periodic heartbeat signals to the C&C server at 500-millisecond intervals.
- Reliable Delivery: Because UDP doesn’t guarantee packet delivery, GhostPenguin implements its own reliability layer, storing outgoing packets and retransmitting them until the server acknowledges receipt.
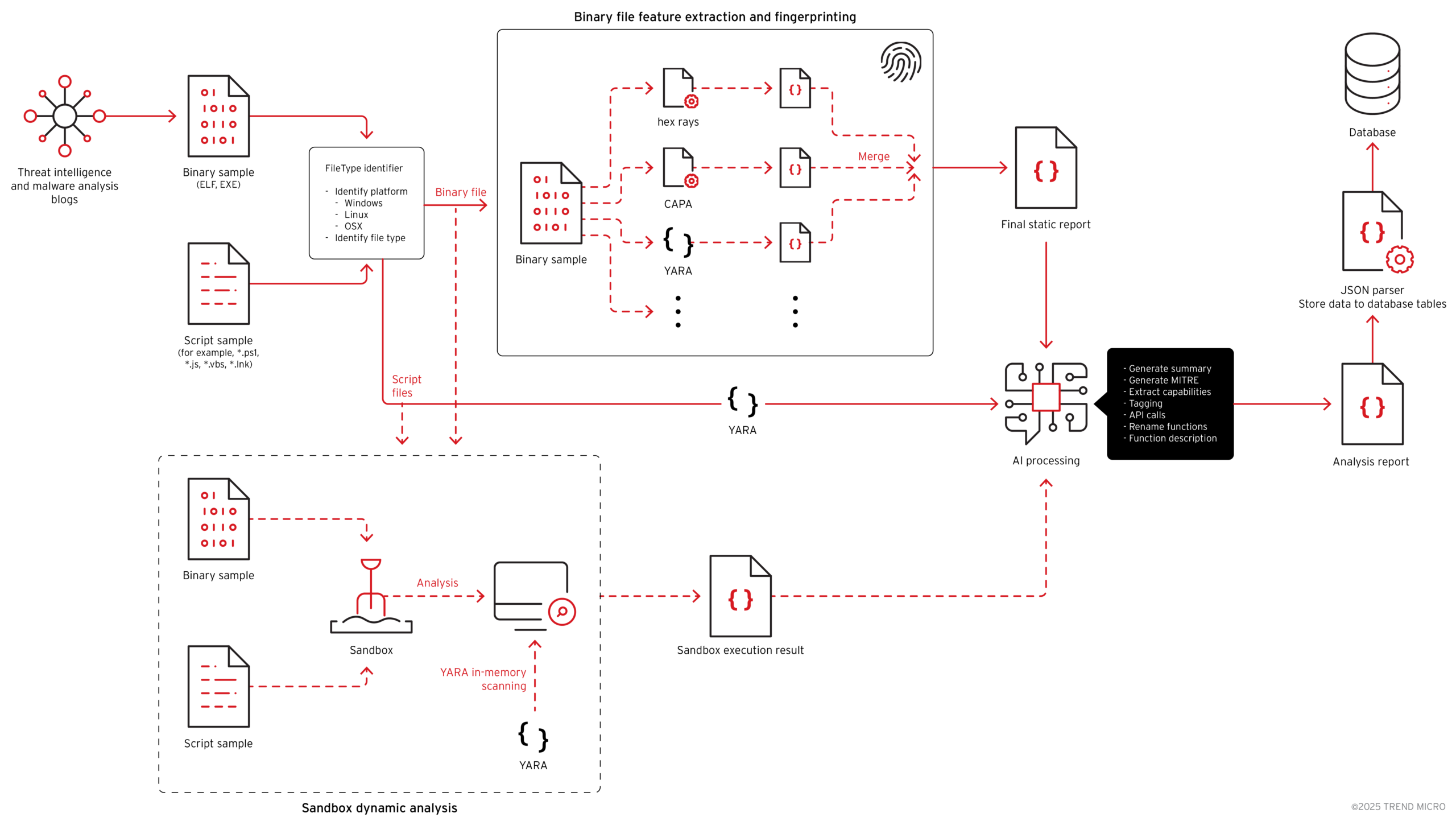
(Threat Intelligence Collection System – Source: Trend Research)
 Severity Assessment
Severity Assessment
The severity of GhostPenguin should not be underestimated, particularly for organizations running Linux infrastructure:
- Zero-Detection Status: The malware evaded all antivirus engines on VirusTotal for over four months, demonstrating exceptional evasion capabilities.
- Full Remote Access: Attackers gain complete remote shell access through /bin/sh, enabling arbitrary command execution on compromised systems.
- Comprehensive File Operations: The backdoor supports approximately 40 different commands covering file creation, deletion, reading, writing, renaming, timestamp modification, and directory-wide searches.
- Data Exfiltration Risk: With full file system access and network communication capabilities, sensitive business data faces significant exposure.
- Active Development: Debug artifacts and unused persistence functions in the code suggest the malware is still under active development, meaning more capabilities may emerge.
 Attack Methodology
Attack Methodology
GhostPenguin follows a methodical infection and operation sequence:
- Initial Execution: The malware resolves its execution context by obtaining the current user’s home directory and its own executable path using system calls.
- Persistence Check: Before fully initializing, it checks whether another instance is already running by examining the PID stored in its lock file.
- C&C Configuration: The backdoor iterates through a list of pre-configured command-and-control server addresses, attempting to establish communication with each.
- Session Handshake: A 34-byte UDP packet with command type 0x04 initiates the session, with the server responding with the actual encryption key.
- Registration Phase: System information is serialized and transmitted to the C&C server to register the infected host.
- Operational State: Once registration completes, the malware enters an active state, maintaining heartbeats and awaiting commands.
- Command Execution: Remote operators can execute shell commands, manipulate files and directories, search for specific file types, and modify timestamps to cover their tracks.
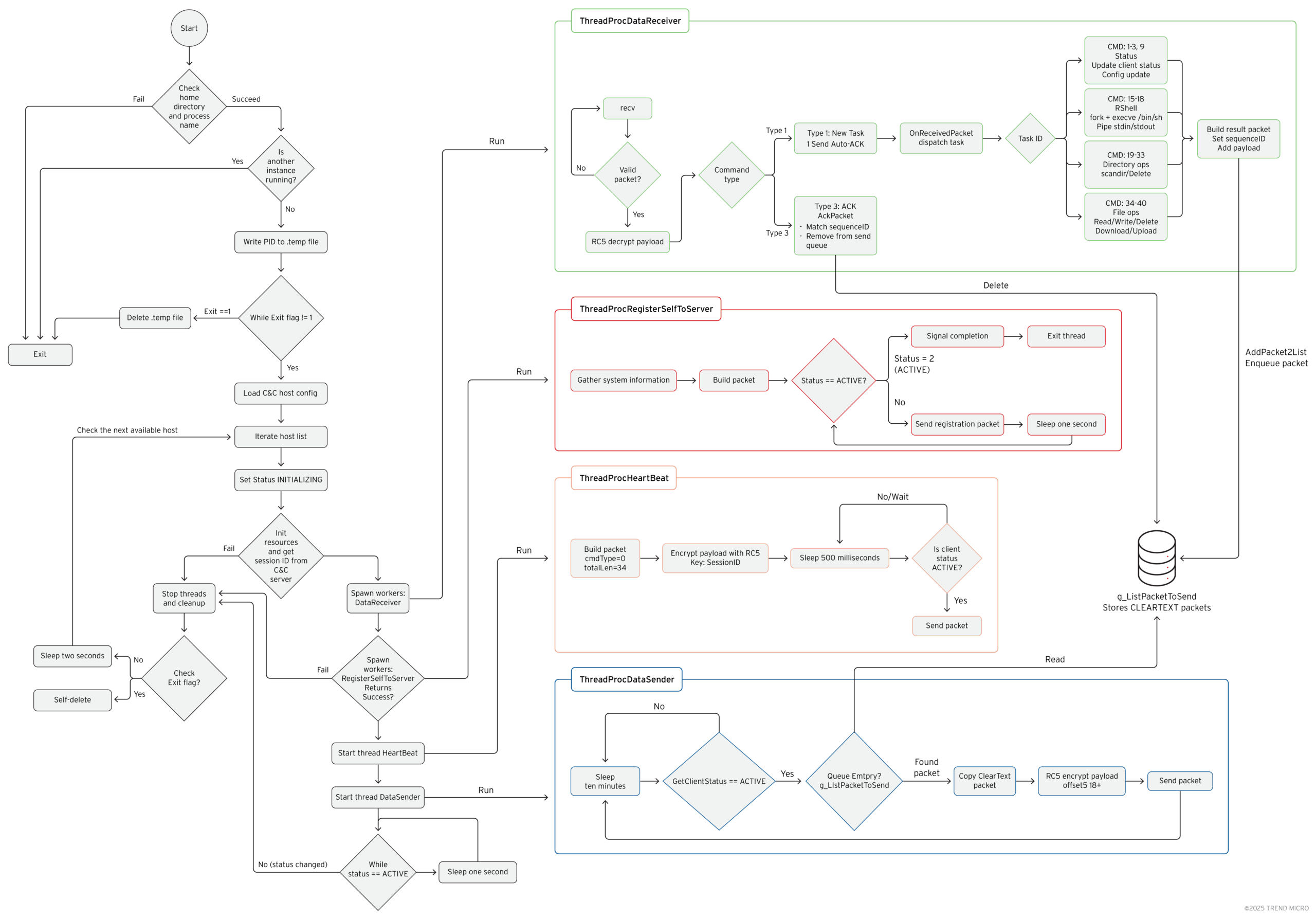
(Malware’s internal architecture – Source: Trend Research)
 Threat Attribution
Threat Attribution
At this time, no specific threat actor or nation-state group has been definitively linked to GhostPenguin. However, several indicators suggest this is not the work of amateur hackers:
- Custom Development: The complete absence of publicly available libraries or borrowed code suggests a well-resourced operation with skilled developers.
- Operational Security: The careful design of minimal network communication and encrypted channels indicates an understanding of detection avoidance.
- Spelling Errors: Interestingly, the code contains several misspellings (“ImpPresistence,” “Userame,” “IsPorecessExistByPID”), potentially indicating non-native English-speaking developers.
- Debug Artifacts: A leftover debug configuration containing a separate domain and IP address suggests structured development and testing processes.
 Who Is at Risk
Who Is at Risk
Organizations operating Linux servers face the primary risk from GhostPenguin:
- Web Hosting Providers: Linux servers hosting websites and applications represent attractive targets for data theft and lateral movement.
- Cloud Infrastructure: Organizations running containerized workloads or virtual machines on Linux-based cloud platforms.
- Enterprise Data Centers: Companies maintaining on-premises Linux servers for databases, file storage, or application services.
- Healthcare and Finance: Industries handling sensitive data on Linux systems face elevated risk given the malware’s file exfiltration capabilities.
- Small and Medium Businesses: Organizations with limited IT security resources that may rely heavily on traditional antivirus solutions.
- Development Environments: Companies using Linux for software development where source code and intellectual property could be compromised.
 Indicators of Compromise
Indicators of Compromise
Security teams should monitor for the following indicators associated with GhostPenguin:
- File Hash: SHA-256: 7b75ce1d60d3c38d7eb63627e4d3a8c7e6a0f8f65c70d0b0cc4756aab98e9ab7
- Process Name: The malware may masquerade as “systemd” to blend with legitimate system processes.
- Hidden File: Presence of “.temp” file in user home directories containing a PID value.
- Network Traffic: UDP communications over port 53 to suspicious external IP addresses.
- C&C Servers: 65.20.72.101:53, www.iytest.com:5679, 124.221.109.147:5679
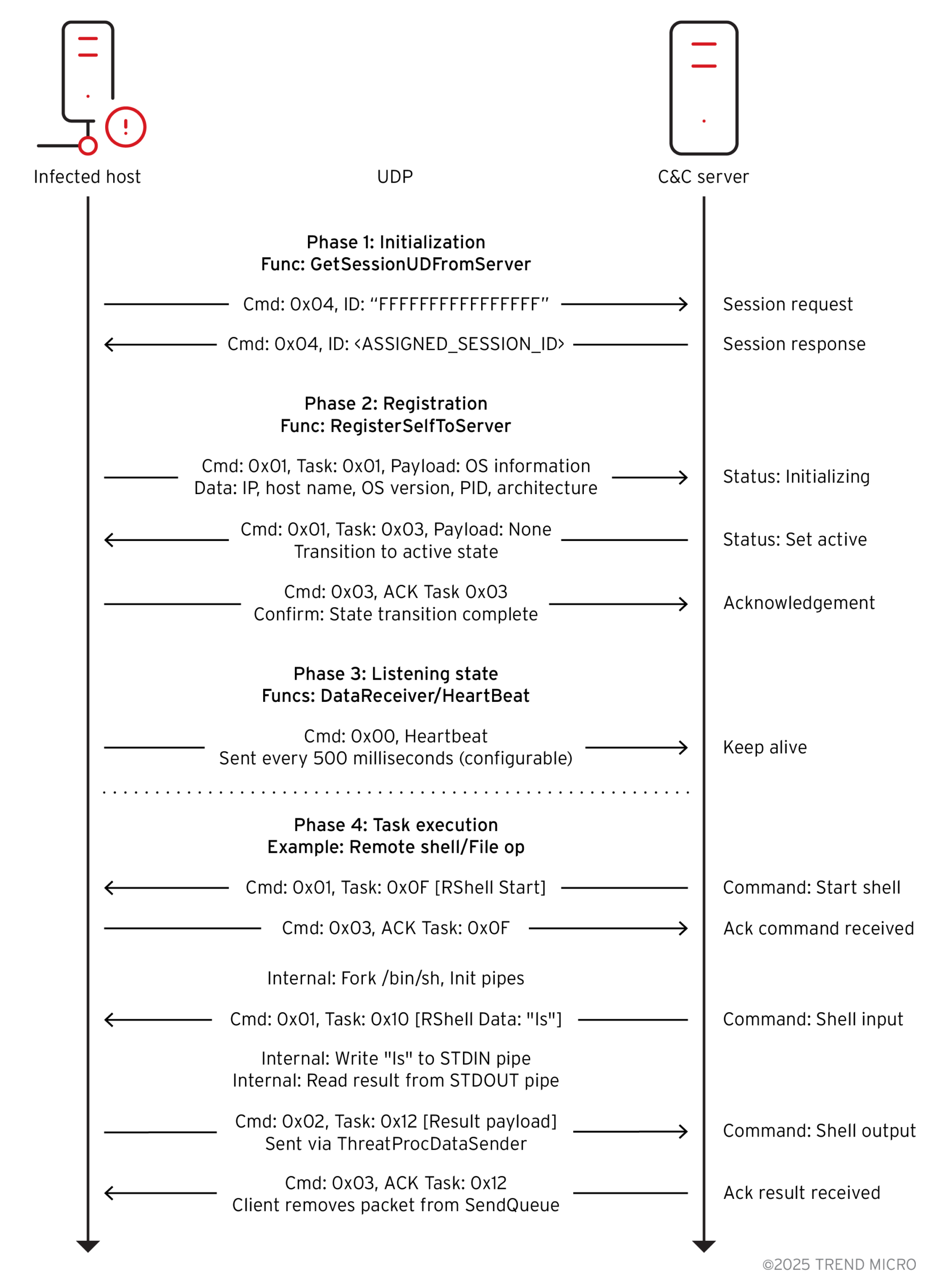
(Network Communication Workflow – Source: Trend Research)
 Remediation and Protection Strategies
Remediation and Protection Strategies
Given GhostPenguin’s ability to evade traditional security tools, organizations should implement layered defenses:
- Network Monitoring: Deploy tools capable of analyzing DNS and UDP traffic patterns for anomalous behavior, particularly unexpected outbound connections on port 53.
- Behavioral Analysis: Implement endpoint detection and response solutions that identify suspicious process behaviors rather than relying solely on signature matching.
- File Integrity Monitoring: Monitor for unexpected hidden files in user home directories, particularly those containing process IDs.
- Access Controls: Limit user privileges and implement least-privilege principles to reduce the impact of successful compromises.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate critical Linux servers and implement strict egress filtering to limit C&C communication opportunities.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic security assessments of Linux infrastructure, including process listing and network connection reviews.
- Threat Intelligence: Subscribe to threat intelligence feeds and update detection rules as new indicators emerge.
The discovery of GhostPenguin through AI-driven analysis rather than traditional detection methods sends a clear message: the security tools of yesterday may not protect against the threats of tomorrow.
 How CinchOps Can Help
How CinchOps Can Help
Discovering that a sophisticated backdoor like GhostPenguin evaded every major antivirus engine for over four months is sobering news for any business relying on Linux infrastructure. At CinchOps, we understand that small and medium-sized businesses in Houston need security that goes beyond traditional signature-based detection.
- Advanced Endpoint Detection and Response: We deploy modern EDR solutions that monitor behavioral patterns and anomalies rather than relying solely on known malware signatures.
- Network Security Monitoring: Our managed IT support includes continuous monitoring of network traffic to identify suspicious communication patterns like those used by GhostPenguin.
- Firewall and Egress Filtering: We implement and manage network security controls that limit outbound communications to authorized destinations only.
- 24/7 Threat Monitoring: As your managed services provider, we provide round-the-clock monitoring to catch threats before they can cause damage.
- Incident Response Planning: We help Houston businesses develop and test response plans so you’re prepared when sophisticated threats emerge.
- Security Awareness Training: We educate your team on recognizing threats and following security best practices to reduce your overall risk exposure.
Don’t wait for a zero-detection threat to compromise your business. Contact CinchOps today for a comprehensive security assessment of your IT infrastructure.
![]()
 Discover More
Discover More 
Discover more about our enterprise-grade and business protecting cybersecurity services: CinchOps Cybersecurity
Discover related topics: The AI-Fication of Cyberthreats: What Houston Businesses Need to Know
For Additional Information on this topic: AI-Automated Threat Hunting Brings GhostPenguin Out of the Shadows
![]()
FREE CYBERSECURITY ASSESSMENT



